Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsushita, Kentaro; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Uchida, Mao*; Sakai, Takaaki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 6 Pages, 2021/05
For the gas entrainment vortex at the free surface in sodium-cooled fast reactors, development of the numerical analysis method to evaluate amount of the gas entrainment from the free surface has been developing. In this paper, the automatic creation of analysis meshes which can suppress the calculation cost while maintaining the prediction accuracy of the vortex shape is investigated, and the adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) method is examined to the creation of analysis mesh applying to the unsteady vortex system. The refined mesh based on the criterion evaluated by vorticity, Q-value as second invariant of the velocity and the discriminant for the eigen equation of the velocity gradient tensor is considered, and it found that the AMR method based on Q-value can refine the analysis meshes most efficiently.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ali, Y.*; Shimokawabe, Takashi*
Proceedings of 9th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA 2018) (Internet), p.9 - 16, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:94.51(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)We develop a communication reduced multi-time- step (CRMT) algorithm for a Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) based on a block-structured adaptive mesh refinement (AMR). This algorithm is based on the temporal blocking method, and can improve computational efficiency by replacing a communication bottleneck with additional computation. The proposed method is implemented on an extreme scale airflow simulation code CityLBM, and its impact on the scalability is tested on GPU based supercomputers, TSUBAME and Reedbush. Thanks to the CRMT algorithm, the communication cost is reduced by 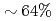 , and weak and strong scalings are improved up to
, and weak and strong scalings are improved up to 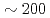 GPUs. The obtained performance indicates that real time airflow simulations for about 2km square area with the wind speed of
GPUs. The obtained performance indicates that real time airflow simulations for about 2km square area with the wind speed of 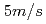 is feasible using 1m resolution.
is feasible using 1m resolution.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 10776, p.128 - 145, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:85.61(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)We developed a CFD code based on the adaptive mesh-refined Lattice Boltzmann Method (AMR-LBM). The code is developed on the GPU-rich supercomputer TSUBAME3.0 at the Tokyo Tech, and the GPU kernel functions are tuned to achieve high performance on the Pascal GPU architecture. The performances of weak scaling from 1 nodes to 36 nodes are examined. The GPUs (NVIDIA TESLA P100) achieved more than 10 times higher node performance than that of CPUs (Broadwell).
Sogabe, Joji; Wada, Yusaku*; Suzuki, Toru*; Tobita, Yoshiharu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Onodera, Naoyuki
no journal, ,
An adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) method is one of the effective methods to compute certain local regions that demand higher accuracy with higher resolution. To develop the applications adopting AMR effectively with maintaining high performance on multiple GPUs, we are developing a block-based AMR framework for stencil applications written in C++ and CUDA. The programmer simply describes a C++11 lambda that updates a grid point, which is applied to the entire grids with various resolution over a tree-based AMR data structure effectively. The framework-based application for compressible flow has demonstrated good weak scalability with 84% of the parallel efficiency on the TSUBAME3.0 GPU supercomputer at Tokyo Institute of Technology.
Sitompul, Y.*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Watanabe, Seiya*; Sugihara, Kenta; Takaki, Tomohiro*
no journal, ,
A cumulant Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) with Multiphase Field (MPF) and Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) has been developed to model foam formation with stable thin liquid films. The proposed method has been successfully employed to simulate 3D foam formation with many bubbles, maintaining mass conservation and using a large density ratio. In addition, we have extended the proposed method to include heat transfer calculations. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the foam as a thermal insulation layer, we simulated 2D foam formation and compared the heat transfer in a cup of water with and without foam. Preliminary results show that the foam effectively acts as a thermal insulator, retaining the water temperature by preventing the natural air convection and acting like a stagnant air layer.